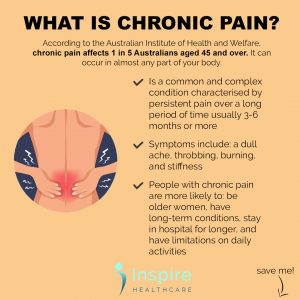
What is Chronic Pain?
Chronic pain is persistent pain that lasts for an extended period of time, typically beyond the expected healing time. Chronic pain can usually last 3-6 months or even longer. Examples include frequent headaches, and lower back pain and interferes with your daily activities, such as working, having a social life and taking care of yourself or others.
What causes chronic pain?
Common causes of chronic pain typically stem from past injuries or surgeries or diseases such as back injuries or strains, arthritis, and infections can cause chronic pain. However, it can sometimes begin without a distinct reason and can be triggered by stress, anxiety and depression. Healthcare providers refer to this as psychogenic pain or psychosomatic pain. Chronic pain can cause mental distress as it interferes with daily life, so it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible. Symptoms of chronic pain may include persistent dull aches, shooting or burning sensations, stiffness, fatigue, sleep disturbances, mood changes, and reduced mobility.
What’s the difference between chronic pain and acute pain?
Acute pain is temporary and typically lasts for a short duration, often directly resulting from an injury or illness. It serves as a warning sign and resolves once the underlying cause heals. Chronic pain persists beyond the expected healing time, lasting for months or even years. It can stem from conditions like arthritis or nerve damage, or in some cases may not be directly linked to recent events. Chronic pain involves a combination of persistent tissue damage, inflammation, and nerve dysfunction.
Common types of chronic pain
Chronic pain can originate from any body part or a combination of areas together. Some common types of chronic pain may come from:
- Back and Spine: Herniated discs, spinal stenosis, degenerative disc disease, or persistent muscle strain can lead to chronic back pain, particularly common in the lower back.
- Joints: Knees, hips, shoulders, or ankles, due to conditions like osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or repetitive stress injuries.
- Head and Neck: Headaches and migraines, or neck pain can result from factors like tension, poor posture, cervical disc problems, or temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJ).
- Nerves: Sciatica, neuropathy, or nerve compression (e.g., carpal tunnel syndrome) and are often characterized by tingling, numbness, or shooting pain.
- Muscles and Soft Tissues: Chronic pain in muscles and soft tissues can stem from fibromyalgia, myofascial pain syndrome, chronic fatigue syndrome, or repetitive strain injuries.
- Pelvic Region: Conditions like endometriosis, chronic pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), or interstitial cystitis can cause chronic pain in the pelvic area.
- Abdomen: Chronic abdominal pain can be caused by conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), or gastrointestinal disorders.
- Nociceptive Pain: Chronic pain can also arise from persistent tissue damage or inflammation caused by injuries, surgeries, or medical conditions affecting organs, bones, or other body structures.
Types of healthcare specialists that can help with diagnosing and treating chronic pain
Specialists who can help with chronic pain include:
- Pain Management Physicians: Experts in diagnosing and treating chronic pain using various techniques.
- Neurologists: Specialize in nerve-related conditions like neuropathy and migraines.
- Rheumatologists: Specialize in joint and autoimmune disorders associated with chronic pain.
- Orthopedic Surgeons: Address musculoskeletal issues contributing to chronic pain.
- Physiotherapists: Provide exercises and therapies to manage pain and improve mobility.
- Psychologists/Psychiatrists: Address the psychological aspects of chronic pain and provide coping strategies.
- Integrative Medicine Specialists: Combine conventional medicine with complementary approaches like acupuncture or herbal medicine.
- Pain Psychologists: Focus on the psychological aspects of chronic pain management.
- Anesthesiologists: Offer interventional procedures for pain relief.
- Primary Care Physicians: Coordinate care, prescribe medications, and provide ongoing support.
Collaborating with a multidisciplinary team ensures comprehensive chronic pain management tailored to individual needs.
Inspire Healthcare are a multi-disciplinary professional healthcare agency, book an appointment with a mobile NDIS Physiotherapist in Sydney or a Physiotherapist in Melbourne
Author
-

Guyver Mac
Managing Director & Principal PhysiotherapistGuyver specialises in gerontology and neurological physiotherapy, and has been working with NDIS since 2017 and practicing physiotherapy since 2015. He excels in treating conditions like Multiple Sclerosis (MS), stroke, neurological conditions, and global developmental delay. One of Guyver's favourite career moments as a physio is helping an Inspire Healthcare client with Multiple Sclerosis walk his daughter down the aisle at her wedding. Outside of work, Guyver enjoys going to the gym, swimming, and watching rugby league.